The connection between physical and mental health is increasingly recognized as crucial to overall well-being. While traditionally treated as separate entities, physical and mental health are deeply interconnected. A decline in one can significantly affect the other, and fostering both is essential for achieving a balanced and healthy life.
This article explores the intricate relationship between physical and mental health, explaining how they influence each other, the biological and psychological mechanisms involved, and strategies to promote a holistic approach to well-being.
What is Physical Health?
Physical health refers to the state of the body and its ability to function efficiently. Key components include:
- Proper nutrition
- Regular exercise
- Adequate sleep
- Disease prevention and management
Maintaining physical health supports your body in managing daily tasks, recovering from illness, and preventing chronic diseases.
What is Mental Health?
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, and behave in daily life. Core aspects include:
- Emotional regulation
- Stress management
- Social connections
- Cognitive functioning
Good mental health is essential for decision-making, problem-solving, and maintaining positive relationships.
The Interconnection Between Physical and Mental Health
1. The Mind-Body Connection
The mind and body communicate through the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems. Emotions and thoughts can influence physical functions, while physical conditions impact mental well-being.
For instance, chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, which, over time, can weaken the immune system and lead to physical ailments like hypertension or diabetes.
2. Shared Risk Factors
Lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, and substance abuse can harm both physical and mental health. These risk factors often overlap, creating a cycle of declining health.
How Physical Health Affects Mental Health
1. Exercise and Mental Health
Regular physical activity improves mental health by:
- Releasing endorphins, which boost mood
- Reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety
- Enhancing cognitive function and memory
2. Nutrition and Brain Function
A balanced diet provides essential nutrients for brain health. Deficiencies in vitamins like B12 or omega-3 fatty acids can lead to mood disorders.
3. Sleep and Emotional Regulation
Poor sleep quality disrupts emotional regulation and increases the risk of mental health issues like anxiety and depression.
4. Chronic Illness and Psychological Impact
Living with chronic physical conditions often leads to mental health challenges. Pain, limited mobility, and the stress of managing illness can result in depression or anxiety.
How Mental Health Affects Physical Health
1. Stress and Physical Ailments
Chronic stress is linked to various physical conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Immune suppression
2. Depression and Lifestyle Choices
Depression can lead to unhealthy behaviors like overeating, smoking, or neglecting exercise, exacerbating physical health problems.
3. Anxiety and Physical Symptoms
Anxiety often manifests physically, causing symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, or gastrointestinal discomfort.
4. Social Isolation and Mortality Risk
Mental health conditions like depression can lead to social withdrawal, which is associated with a higher risk of mortality due to physical health neglect.
Biological Mechanisms Linking Physical and Mental Health
1. Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a shared factor in conditions like depression, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Psychological stress triggers inflammatory responses, which, in turn, affect physical health.
2. Hormonal Pathways
Hormones like cortisol (stress hormone) and serotonin (mood regulator) play dual roles in physical and mental health. Imbalances can lead to conditions like anxiety or fatigue.
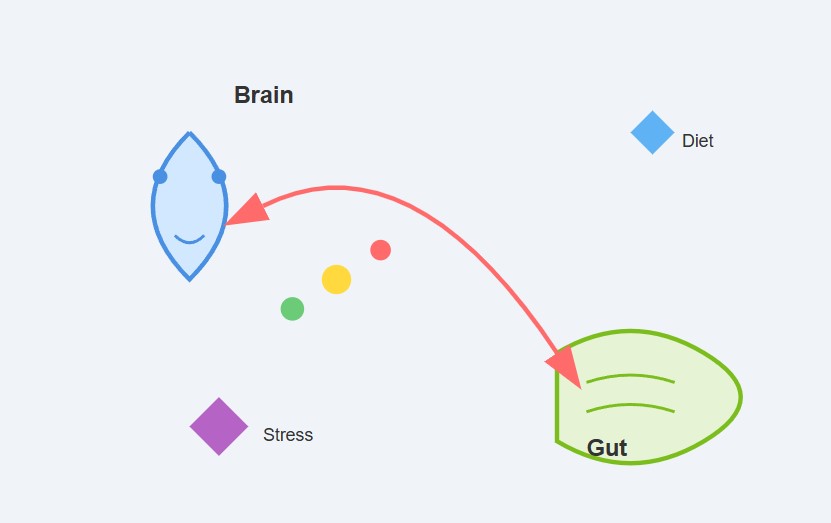
3. Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis highlights the connection between gut microbiota and mental health. Poor gut health can contribute to mood disorders, while stress can disrupt gut function.
Promoting a Holistic Approach to Health
To optimize physical and mental health, a balanced approach is essential.
1. Regular Physical Activity
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily.
- Incorporate activities you enjoy to stay motivated.
2. Balanced Nutrition
- Focus on whole foods rich in essential nutrients.
- Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods that can harm mental and physical health.
3. Quality Sleep
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Create a sleep-conducive environment, free from distractions.
4. Stress Management
- Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- Engage in hobbies that bring joy and reduce stress.
5. Build Supportive Relationships
- Nurture connections with family and friends.
- Seek professional support when needed.
6. Regular Checkups
- Monitor physical health with regular medical checkups.
- Address mental health concerns with a qualified professional.
Challenges in Maintaining Both Physical and Mental Health
1. Stigma Around Mental Health
Social stigma often prevents individuals from seeking help for mental health issues, which can exacerbate physical conditions.
2. Access to Healthcare
Limited access to affordable healthcare can hinder proper diagnosis and treatment of interconnected health issues.
3. Lack of Awareness
Many people are unaware of the connection between physical and mental health, leading to neglect of one aspect.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in addressing the link between physical and mental health by:
- Offering integrated care that addresses both aspects
- Educating patients on the connection between their mind and body
- Encouraging preventive measures and lifestyle changes
Future Directions in Holistic Health
1. Technology and Health Tracking
Wearable devices and apps can monitor physical activity, sleep, and stress levels, helping individuals maintain balance.
2. Public Health Campaigns
Awareness campaigns can reduce stigma and educate people about the connection between physical and mental health.
3. Research on Interventions
Ongoing research is exploring interventions like mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and its impact on both mental and physical health.
Conclusion
The link between physical and mental health is undeniable and complex. By understanding this connection, individuals can take proactive steps to care for their overall well-being. Small, consistent lifestyle changes—such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management—can create a ripple effect, improving both physical and mental health.
Investing in holistic health not only enhances quality of life but also ensures resilience in the face of life’s challenges.